Append Numpy Array
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. Appending to a Numpy array is a common operation that can be performed in various ways depending on the requirement. In this article, we will explore different methods to append data to Numpy arrays, along with detailed examples.
Appending Elements to a 1D Array
Appending elements to a one-dimensional array can be done using the numpy.append() function. This function takes two arrays as input and returns a new array with the elements of the second array appended to the first array.
Example 1: Appending a Single Element
import numpy as np
# Original array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# Append a single element
arr = np.append(arr, 4)
print(arr)
Output:
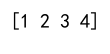
Example 2: Appending Multiple Elements
import numpy as np
# Original array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# Append multiple elements
arr = np.append(arr, [4, 5, 6])
print(arr)
Output:
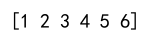
Appending Arrays Along an Axis
When working with multi-dimensional arrays, you can append arrays along a specific axis using the numpy.append() function by specifying the axis parameter.
Example 3: Appending Arrays Along Axis 0
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6]])
# Append arr2 to arr1 along axis 0
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2, axis=0)
print(arr)
Output:

Example 4: Appending Arrays Along Axis 1
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5], [6]])
# Append arr2 to arr1 along axis 1
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2, axis=1)
print(arr)
Output:

Using numpy.concatenate() to Append Arrays
The numpy.concatenate() function is another way to join two arrays along an existing axis.
Example 5: Concatenating 1D Arrays
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
Output:
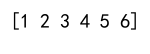
Example 6: Concatenating 2D Arrays Along Axis 0
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6]])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2 along axis 0
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=0)
print(arr)
Output:

Example 7: Concatenating 2D Arrays Along Axis 1
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2 along axis 1
arr = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=1)
print(arr)
Output:

Using numpy.vstack() and numpy.hstack() for Stacking Arrays
Numpy provides functions like numpy.vstack() for vertical stacking and numpy.hstack() for horizontal stacking of arrays.
Example 8: Vertical Stacking Using vstack()
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Vertically stack arr1 and arr2
arr = np.vstack((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
Output:

Example 9: Horizontal Stacking Using hstack()
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1], [2], [3]])
arr2 = np.array([[4], [5], [6]])
# Horizontally stack arr1 and arr2
arr = np.hstack((arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
Output:

Appending Arrays Using numpy.r_ and numpy.c_
Numpy also provides the numpy.r_ and numpy.c_ objects for array concatenation along the first and second axis, respectively.
Example 10: Using numpy.r_ for Row Concatenation
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Row concatenation
arr = np.r_[arr1, arr2]
print(arr)
Output:
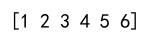
Example 11: Using numpy.c_ for Column Concatenation
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Column concatenation
arr = np.c_[arr1, arr2]
print(arr)
Output:

Appending Arrays with Different Dimensions
When appending arrays of different dimensions, it’s important to match the shape along the axis you are appending.
Example 12: Appending a 1D Array to a 2D Array Along Axis 0
import numpy as np
# Original 2D array
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# Original 1D array
arr2 = np.array([5, 6])
# Append arr2 to arr1 along axis 0
arr = np.append(arr1, [arr2], axis=0)
print(arr)
Output:

Example 13: Appending a 1D Array to a 2D Array Along Axis 1
import numpy as np
# Original 2D array
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# Original 1D array
arr2 = np.array([5, 6])
# Append arr2 to arr1 along axis 1
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2.reshape(2, 1), axis=1)
print(arr)
Output:

Appending with Broadcasting
Numpy’s broadcasting feature allows for appending arrays with different shapes, provided that they are compatible according to broadcasting rules.
Example 14: Broadcasting a Scalar to a 1D Array
import numpy as np
# Original array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# Append a scalar value, broadcasting it
arr = np.append(arr, np.full((1,), 4))
print(arr)
Output:
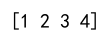
Example 15: Broadcasting a 1D Array to a 2D Array
import numpy as np
# Original 2D array
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# Original 1D array
arr2 = np.array([5, 6])
# Append arr2 to arr1, broadcasting it
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2.reshape(1, 2), axis=0)
print(arr)
Output:

Appending with Flattening
If you want to append arrays and flatten the result into a 1D array, you can use the numpy.append() function without specifying an axis.
Example 16: Appending 2D Arrays with Flattening
import numpy as np
# Two original 2D arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Append arr1 and arr2, flattening the result
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(arr)
Output:
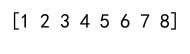
Appending with Reshaping
If you want to append arrays and reshape the result into a different shape, you can use the numpy.append() function followed by the numpy.reshape() function.
Example 17: Appending 1D Arrays with Reshaping
import numpy as np
# Two original 1D arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Append arr1 and arr2, reshaping the result
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2).reshape(2, 3)
print(arr)
Output:

Appending with Type Conversion
If you want to append arrays and convert the type of the result, you can use the numpy.append() function followed by the numpy.astype() function.
Example 18: Appending Integer Arrays with Float Conversion
import numpy as np
# Two original integer arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Append arr1 and arr2, converting the result to float
arr = np.append(arr1, arr2).astype(float)
print(arr)
Output:

Appending with Sorting
If you want to append arrays and sort the result, you can use the numpy.append() function followed by the numpy.sort() function.
Example 19: Appending Arrays with Sorting
import numpy as np
# Two original arrays
arr1 = np.array([3, 2, 1])
arr2 = np.array([6, 5, 4])
# Append arr1 and arr2, sorting the result
arr = np.sort(np.append(arr1, arr2))
print(arr)
Output:
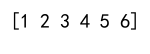
Append Numpy Array Conclusion
In this article, we have covered several ways to append data to Numpy arrays, including appending elements to a 1D array, appending arrays along an axis, using numpy.concatenate(), numpy.vstack(), numpy.hstack(), numpy.r_, and numpy.c_ for array concatenation, appending arrays with different dimensions, broadcasting, flattening, reshaping, type conversion, and sorting. We hope this guide will be helpful for your data manipulation tasks in Python using Numpy. For more information, please visit numpyarray.com.