Numpy Append
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the common operations when working with arrays is appending elements or arrays to an existing array. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to use the numpy.append() function, along with detailed examples.
Introduction to Numpy Append
The numpy.append() function is used to append values to the end of a given array. It returns a new array and does not modify the original array. The syntax of the numpy.append() function is as follows:
numpy.append(arr, values, axis=None)
arr: This is the array to whichvaluesare appended.values: These are the values to be appended. This can be a scalar, list, or another array.axis: This is the axis along which the values are appended. Ifaxisis not specified, botharrandvaluesare flattened before use.
Examples of Numpy Append
Example 1: Appending Scalars to a One-Dimensional Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
values = 4
result = np.append(arr, values)
print(result)
Output:
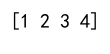
Example 2: Appending a List to a One-Dimensional Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
values = [4, 5, 6]
result = np.append(arr, values)
print(result)
Output:
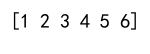
Example 3: Appending an Array to Another Array
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
result = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(result)
Output:
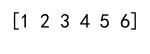
Example 4: Appending with Axis Specified (2D Arrays)
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6]])
result = np.append(arr1, arr2, axis=0)
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Flattening and Appending Arrays
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
result = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(result)
Output:
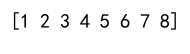
Example 6: Appending Arrays with Different Dimensions
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([[4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
result = np.append(arr1, arr2, axis=0)
print(result)
Example 7: Using Append in a Loop
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
for i in range(4, 7):
arr = np.append(arr, i)
print(arr)
Output:
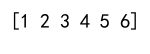
Example 8: Appending Multiple Arrays at Once
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr3 = np.array([7, 8, 9])
result = np.append(np.append(arr1, arr2), arr3)
print(result)
Output:
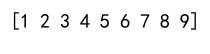
Example 9: Appending Arrays with Different Shapes Using Axis
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([5, 6])
result = np.append(arr1, arr2.reshape(1, 2), axis=0)
print(result)
Output:

Numpy Append Conclusion
The numpy.append() function is a versatile tool for adding elements to numpy arrays. Whether you’re working with one-dimensional or multi-dimensional arrays, understanding how to use numpy.append() effectively can help you manipulate array data more efficiently. The examples provided in this article illustrate various ways to use the numpy.append() function in different scenarios, making it easier to integrate into your data processing workflows.