Numpy Argmax in Two Dimensions
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is argmax, which returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. When working with two-dimensional arrays, understanding how to use argmax effectively can be incredibly useful for data analysis and manipulation.
In this article, we will explore how to use the argmax function in two dimensions, providing detailed examples and explanations to help you master this functionality.
Understanding numpy.argmax
The numpy.argmax function returns the indices of the maximum values along a specified axis. In a two-dimensional array, you can specify whether you want to find the maximum values in rows or columns by setting the axis parameter.
Syntax of numpy.argmax
numpy.argmax(a, axis=None, out=None)
a: Input array.axis: By default, the index is into the flattened array, otherwise along the specified axis.out: If provided, the result will be inserted into this array. It should be of the appropriate shape and dtype.
Example 1: Basic Usage of argmax in a 2D Array
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [6, 2, 8], [7, 9, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array_2d, axis=1)
print(result) # Output will be [2, 2, 1]
Output:
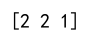
Example 2: Using argmax Without Specifying Axis
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [6, 2, 8], [7, 9, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array_2d)
print(result) # Output will be 5
Output:
![]()
Detailed Examples with numpy.argmax
Let’s dive deeper with more examples to understand the usage of numpy.argmax in various scenarios with two-dimensional arrays.
Example 3: Finding Column Indices of Maximum Values
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[10, 20, 30], [15, 25, 5], [35, 5, 15]])
result = np.argmax(array_2d, axis=0)
print(result) # Output will be [2, 1, 0]
Output:
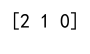
Example 4: Using argmax with a Flattened Array
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[10, 20, 30], [15, 25, 5], [35, 5, 15]])
result = np.argmax(array_2d.flatten())
print(result) # Output will be 6
Output:
![]()
Example 5: Specifying Output Array for Results
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[10, 20, 30], [15, 25, 5], [35, 5, 15]])
output_array = np.empty((3,), dtype=int)
np.argmax(array_2d, axis=1, out=output_array)
print(output_array) # Output will be [2, 1, 0]
Output:
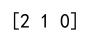
Example 6: Argmax with Randomly Generated Array
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
array_2d = np.random.randint(1, 100, (3, 3))
result = np.argmax(array_2d, axis=1)
print(result) # Output will be [2, 2, 0]
Output:
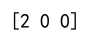
Example 7: Argmax in a Real-World Dataset
import numpy as np
# Simulating a dataset where rows are samples and columns are features
data = np.random.rand(10, 5) * 100
# Finding the feature (column) with the maximum value for each sample (row)
max_feature_indices = np.argmax(data, axis=1)
print(max_feature_indices) # Output will be indices of the max feature per sample
Output:
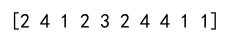
Example 8: Handling Higher Dimensional Data
import numpy as np
data = np.random.rand(2, 3, 4) * 100
# Applying argmax on the last axis of a 3D array
max_indices = np.argmax(data, axis=-1)
print(max_indices) # Output will be a 2x3 array
Output:

Example 9: Using Argmax with Structured Arrays
import numpy as np
dtype = [('name', 'S10'), ('height', float), ('age', int)]
values = [('Alice', 165.3, 34), ('Bob', 175.0, 45), ('Charlie', 155.0, 25)]
structured_array = np.array(values, dtype=dtype)
max_index = np.argmax(structured_array['height'])
print(max_index) # Output will be 1
Output:
![]()
Example 10: Argmax with NaN Values
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[np.nan, 2, np.nan], [3, np.nan, 1], [4, 2, np.nan]])
result = np.nanargmax(array_2d, axis=1)
print(result) # Output will be [1, 0, 0]
Output:
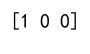
Numpy Argmax in Two Dimensions Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to use the numpy.argmax function in two-dimensional arrays. We provided detailed examples to demonstrate its usage in various scenarios, which should help you apply these techniques in your own data analysis tasks. Understanding how to effectively use argmax can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and manipulate data using Numpy.