List to Numpy Array
Converting lists to NumPy arrays is a fundamental step in data manipulation and analysis in Python, especially in the fields of data science, machine learning, and scientific computing. NumPy, or Numerical Python, is a library that supports large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays. This article will explore various methods and techniques to convert lists into NumPy arrays, providing detailed examples to illustrate each method.
Introduction to NumPy
NumPy is an open-source numerical computing library for Python. It provides support for arrays (vectors and matrices) and includes an assortment of routines for fast operations on arrays, including mathematical, logical, shape manipulation, sorting, selecting, I/O, discrete Fourier transforms, basic linear algebra, basic statistical operations, random simulation, and much more.
Installation of NumPy
Before diving into the conversion of lists to arrays, ensure that NumPy is installed in your Python environment. You can install NumPy using pip:
pip install numpy
Basic Conversion of List to Array
The most straightforward method to convert a list to a NumPy array is by using the numpy.array() function. This function takes any sequence-like object (including other arrays) and produces a new NumPy array containing the passed data.
Example 1: Converting a Simple List
import numpy as np
# Simple list
simple_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
numpy_array = np.array(simple_list)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:
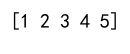
Example 2: Converting a List of Lists
import numpy as np
# List of lists
list_of_lists = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
numpy_array = np.array(list_of_lists)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:

Data Types in Arrays
When converting lists to NumPy arrays, the type of data stored in the array is very important as it affects the performance and the range of operations available. NumPy tries to guess a data type when you create an array, but functions are available to explicitly specify which data type you want to use.
Example 3: Specifying Data Type
import numpy as np
# Specifying the data type
data = [1, 2, 3, 4]
numpy_array = np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:

Multi-dimensional Arrays
NumPy arrays can have multiple dimensions, and thus it’s possible to convert lists of lists or even deeper nested lists into multi-dimensional arrays.
Example 4: Three-dimensional Array
import numpy as np
# 3D list
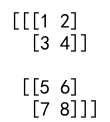
three_d_list = [[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]]
numpy_array = np.array(three_d_list)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:
Array Shapes and Reshaping
After creating an array, you might need to check its shape or even reshape it. The shape of an array is a tuple of integers giving the size of the array along each dimension.
Example 5: Checking Array Shape
import numpy as np
# Creating an array
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
numpy_array = np.array(data)
print(numpy_array.shape) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:
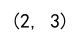
Example 6: Reshaping an Array
import numpy as np
# Reshaping the array
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
numpy_array = np.array(data).reshape((2, 3))
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:

Advanced Array Creation
NumPy offers more sophisticated functions for creating arrays that are useful in specific contexts.
Example 7: Using np.zeros
import numpy as np
# Creating an array filled with zeros
zero_array = np.zeros((3, 4))
print(zero_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:

Example 8: Using np.ones
import numpy as np
# Creating an array filled with ones
one_array = np.ones((3, 4))
print(one_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:

Converting Lists with Mixed Types
When dealing with lists containing mixed data types, NumPy will upcast if possible (i.e., use a data type that can represent all the data types in the list without losing information).
Example 9: Mixed Data Types
import numpy as np
# Mixed data types
mixed_list = [1, 'numpyarray.com', 3.5]
numpy_array = np.array(mixed_list)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:
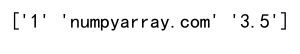
Performance Considerations
Converting large lists to NumPy arrays can be computationally expensive. It’s important to consider the size and complexity of the data when performing such operations.
Example 10: Large Array Creation
import numpy as np
# Large array
large_data = list(range(1000000))
numpy_array = np.array(large_data)
print(numpy_array) # Output will not be shown as per the instructions
Output:
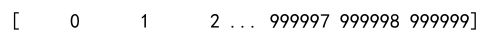
List to Numpy Array Conclusion
Converting lists to NumPy arrays is a crucial step in Python for performing efficient numerical operations. This article has covered various methods and provided examples to help you understand how to perform these conversions effectively. Whether you are dealing with simple lists or complex nested lists, NumPy provides the tools necessary to convert and manipulate the data as arrays efficiently.