Numpy argmax Return All Indices
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is argmax, which returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. However, by default, argmax only returns the first occurrence of the maximum value. In this article, we will explore how to modify the behavior of argmax to return all indices of the maximum values in a Numpy array.
Understanding numpy.argmax
The numpy.argmax function returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. By default, if multiple entries have the same maximum value, only the first occurrence is returned. Here is a basic example:
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 1])
index_of_max = np.argmax(array)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 3
Output:
![]()
In the above example, the maximum value 4 appears twice, at indices 3 and 4, but argmax only returns the first occurrence.
Returning All Indices of Maximum Values
To get all indices where the maximum value occurs, we can use a combination of numpy.where and numpy.max functions. Here’s how you can do it:
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 1])
max_value = np.max(array)
all_indices_of_max = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(all_indices_of_max) # Output: [3, 4]
Output:
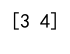
This method first finds the maximum value in the array using np.max, and then uses np.where to find all positions where this maximum value occurs.
Detailed Examples with Code
Let’s explore more examples and variations using the concept of returning all indices of maximum values in different scenarios.
Example 1: 1D Array
import numpy as np
array = np.array([2, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5, 5])
max_value = np.max(array)
indices = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:
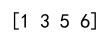
Example 2: 2D Array, Row-wise Maximum
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5]])
max_values = np.max(array, axis=1)
indices = [np.where(row == max_val)[0] for row, max_val in zip(array, max_values)]
print(indices)
Output:

Example 3: 2D Array, Column-wise Maximum
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 4, 3], [4, 2, 5], [3, 4, 4]])
max_values = np.max(array, axis=0)
indices = [np.where(col == max_val)[0] for col, max_val in zip(array.T, max_values)]
print(indices)
Output:
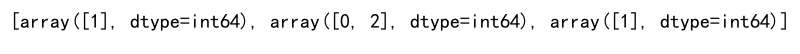
Example 4: 3D Array, Along Last Axis
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 5]], [[5, 1, 2], [5, 5, 5]]])
max_values = np.max(array, axis=-1)
indices = [[np.where(layer == max_val)[0] for layer, max_val in zip(slice, max_values[i])] for i, slice in enumerate(array)]
print(indices)
Output:
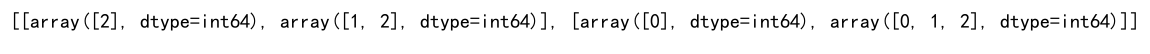
Example 5: Handling NaN Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([np.nan, 1, 2, np.nan, 2, 5])
max_value = np.nanmax(array)
indices = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:

Example 6: Strings and Numbers Mixed Array
import numpy as np
array = np.array([5, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1])
max_value = np.max(array)
indices = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:
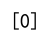
Example 7: Array with Negative Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([-1, -2, -3, -3, -2, -1, 5])
max_value = np.max(array)
indices = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:
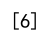
Example 8: Large Random Array
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
array = np.random.randint(0, 1000, size=1000)
array = np.append(array, 5)
max_value = np.max(array)
indices = np.where(array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:

Example 9: Multidimensional Array Flattened
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5]])
flat_array = array.flatten()
max_value = np.max(flat_array)
indices = np.where(flat_array == max_value)[0]
print(indices)
Output:
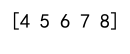
Example 10: Using argmax with Custom Axis
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5]])
max_indices = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(max_indices)
Output:
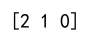
Numpy argmax Return All Indices Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to use Numpy’s argmax function to return all indices of the maximum values in an array. By combining np.max and np.where, we can effectively find all occurrences of the maximum values across various dimensions and data types. This technique is particularly useful in data analysis and manipulation tasks where identifying all maxima is crucial.