Numpy Argmax of Matrix
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is argmax, which returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. In this article, we will explore how to use the argmax function in various scenarios with matrices.
Understanding numpy.argmax
The numpy.argmax function returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. This can be particularly useful when you need to locate the position of the highest value in an array or along a specific axis in a matrix.
Syntax of numpy.argmax
numpy.argmax(a, axis=None, out=None)
- a: Input array.
- axis: By default, the index is into the flattened array, otherwise along the specified axis.
- out: If provided, the result will be inserted into this array. It should be of the appropriate shape and dtype.
Example 1: Basic Usage of argmax on a 1D Array
import numpy as np
# Creating a 1D array
arr = np.array([1, 3, 2, 7, 4])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output will be 3
Output:
![]()
Example 2: Using argmax on a 2D Array
import numpy as np
# Creating a 2D array
arr = np.array([[1, 3, 2], [7, 4, 5]])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output will be 3 (index in flattened array)
Output:
![]()
Example 3: Using argmax Along an Axis
import numpy as np
# Creating a 2D array
arr = np.array([[1, 3, 2], [7, 4, 5]])
index_of_max_along_axis0 = np.argmax(arr, axis=0)
index_of_max_along_axis1 = np.argmax(arr, axis=1)
print(index_of_max_along_axis0) # Output will be [1, 1, 1]
print(index_of_max_along_axis1) # Output will be [1, 0]
Output:

Practical Examples of Using numpy.argmax
Let’s explore more practical examples where numpy.argmax can be effectively used with matrices.
Example 4: Finding the Maximum Value’s Index in Each Row
import numpy as np
matrix = np.random.randint(1, 10, size=(5, 5))
row_max_indices = np.argmax(matrix, axis=1)
print(row_max_indices)
Output:
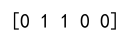
Example 5: Finding the Maximum Value’s Index in Each Column
import numpy as np
matrix = np.random.randint(1, 10, size=(5, 5))
column_max_indices = np.argmax(matrix, axis=0)
print(column_max_indices)
Output:
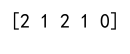
Example 6: Using argmax with a 3D Array
import numpy as np
array_3d = np.random.randint(1, 10, size=(3, 3, 3))
max_index_3d = np.argmax(array_3d, axis=2)
print(max_index_3d)
Output:

Example 7: Using argmax to Determine the Most Frequent Value
import numpy as np
data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5])
counts = np.bincount(data)
most_frequent = np.argmax(counts)
print(most_frequent)
Output:
![]()
Example 8: Using argmax in Image Processing
import numpy as np
# Simulating an image as a 2D array
image = np.random.randint(0, 256, (10, 10))
# Finding the brightest pixel
brightest_pixel_index = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(image), image.shape)
print(brightest_pixel_index)
Output:
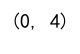
Example 9: Using argmax to Solve a Business Problem
import numpy as np
# Simulating monthly sales data for 5 products
sales_data = np.random.randint(1000, 10000, (12, 5))
# Finding the month with the highest sales for each product
best_month = np.argmax(sales_data, axis=0)
print(best_month)
Output:
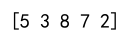
Example 10: Advanced Usage with Structured Arrays
import numpy as np
# Creating a structured array
dtype = [('name', 'S10'), ('height', float), ('age', int)]
values = [('Alice', 1.62, 40), ('Bob', 1.85, 32), ('Charlie', 1.75, 29)]
structured_array = np.array(values, dtype=dtype)
# Finding the oldest person
oldest_index = np.argmax(structured_array['age'])
print(structured_array[oldest_index]['name'])
Output:
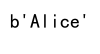
Numpy Argmax of Matrix Conclusion
In this article, we explored the numpy.argmax function in detail, discussing its syntax, basic usage, and practical applications in various scenarios. We provided several examples demonstrating how to use argmax to find the maximum values in arrays and matrices, and how it can be applied to solve real-world problems efficiently.