Numpy Argmax of 2D Array
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is argmax, which returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis in an array. In this article, we will explore how to use the argmax function specifically with 2D arrays.
Understanding numpy.argmax
The numpy.argmax function is used to find the indices of the maximum values along a specified axis. For a 2D array, you can find the index of the maximum value in each row or each column, depending on the axis you choose. The function syntax is as follows:
numpy.argmax(a, axis=None, out=None)
a: Input array.axis: By default, the index is into the flattened array, otherwise along the specified axis.out: If provided, the result will be inserted into this array. It should be of the appropriate shape and dtype.
Example 1: Basic Usage of argmax on a 2D Array
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [7, 2, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [2 0]
Output:
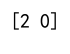
Example 2: Using argmax Without Specifying Axis
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [7, 2, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array)
print(result) # Output: 3
Output:
![]()
Detailed Examples with 2D Arrays
Let’s dive deeper and explore various scenarios and examples using numpy.argmax with 2D arrays.
Example 3: Argmax with Axis 0
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 6, 5], [7, 2, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=0)
print(result) # Output: [1 0 0]
Output:
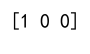
Example 4: Argmax with Axis 1
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 6, 5], [7, 2, 8]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [1 2]
Output:
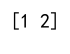
Example 5: Using argmax on a 2D Array with All Negative Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[-1, -6, -5], [-7, -2, -8]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 1]
Output:
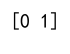
Example 6: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Mixed Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, -6, 5], [-7, 2, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [2 2]
Output:
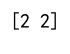
Example 7: Specifying Output Array in argmax
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [7, 2, 4]])
out = np.empty(2, dtype=int)
np.argmax(array, axis=1, out=out)
print(out) # Output: [2 0]
Output:
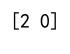
Example 8: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Ties
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 3, 3], [7, 7, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [1 0]
Output:
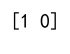
Example 9: Using argmax on a 2D Array with All Same Elements
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Output:
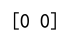
Example 10: Using argmax on a 2D Array with None Axis
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [7, 2, 4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=None)
print(result) # Output: 3
Output:
![]()
Example 11: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Floating Point Numbers
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1.1, 3.5, 2.2], [7.3, 2.8, 4.4]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [1 0]
Output:
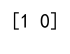
Example 12: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Complex Numbers
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1+1j, 3+3j, 5-5j], [7+7j, 2+2j, 4-4j]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [2 0]
Output:
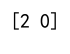
Example 13: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Boolean Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[True, False, True], [False, True, False]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 1]
Output:
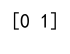
Example 14: Using argmax on a 2D Array with String Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([["numpyarray.com", "numpyarray.com", "numpyarray.com"], ["numpyarray.com", "numpyarray.com", "numpyarray.com"]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Output:
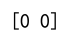
Example 15: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Different Length Strings
import numpy as np
array = np.array([["numpy", "numpyarray.com", "np"], ["numpyarray.com", "numpy", "numpyarray.com"]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [1 0]
Output:
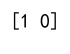
Example 16: Using argmax on a 2D Array with None Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[None, None, None], [None, None, None]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Example 17: Using argmax on a 2D Array with NaN Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[np.nan, np.nan, np.nan], [np.nan, np.nan, np.nan]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Output:
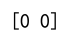
Example 18: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Infinite Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[np.inf, np.inf, np.inf], [np.inf, np.inf, np.inf]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Output:
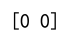
Example 19: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Zero Values
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [0 0]
Output:
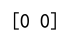
Example 20: Using argmax on a 2D Array with Large Numbers
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1e10, 3e10, 5e10], [7e10, 2e10, 4e10]])
result = np.argmax(array, axis=1)
print(result) # Output: [2 0]
Output:
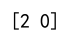
Numpy Argmax of 2D Array Conclusion
In this article,we have explored the numpy.argmax function in detail, specifically with 2D arrays. We have seen how to use it to find the indices of the maximum values along different axes, and how it behaves with different types of data, including negative numbers, floating point numbers, complex numbers, boolean values, strings, None values, NaN values, infinite values, zero values, and large numbers.
Remember that numpy.argmax returns the first occurrence of the maximum value, in case of ties. Also, when the axis is not specified, the function operates on the flattened array.
The numpy.argmax function is a powerful tool that can be used in many data analysis tasks. It is particularly useful when you need to find the location of the maximum value in an array, which is a common requirement in machine learning and statistics.