Numpy Argmax
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is argmax. This function is used to find the indices of the maximum values along an axis in an array.
Understanding Numpy Argmax
The numpy.argmax() function returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis. This can be incredibly useful when you need to locate the position of the highest value in an array or along a specific axis in a multidimensional array.
Syntax of Numpy Argmax
numpy.argmax(a, axis=None, out=None)
- a: Input array.
- axis: By default, the index is into the flattened array, otherwise along the specified axis.
- out: If provided, the result will be inserted into this array. It should be of the appropriate shape and dtype.
Examples of Using Numpy Argmax
Example 1: Find the index of the maximum value in a 1D array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 3, 2, 7, 4])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 3
Output:
![]()
Example 2: Use argmax on a 2D array without specifying an axis
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 6, 5]])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 4 (Flattened index)
Output:
![]()
Example 3: Use argmax on a 2D array along axis 0
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 6, 5]])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr, axis=0)
print(index_of_max) # Output: [1 1 1]
Output:
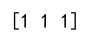
Example 4: Use argmax on a 2D array along axis 1
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 6, 5]])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr, axis=1)
print(index_of_max) # Output: [2 1]
Output:
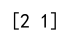
Example 5: Using argmax with a 3D array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr, axis=2)
print(index_of_max) # Output: [[1 1] [1 1]]
Output:

Example 6: Using argmax on an array with NaN values
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([np.nan, 1, 2, np.nan])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 2 (NaN is treated as very small)
Output:
![]()
Example 7: Using argmax on an array with all elements the same
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([7, 7, 7, 7])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 0 (First occurrence is returned)
Output:
![]()
Example 8: Using argmax on an empty array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([])
try:
print(np.argmax(arr))
except ValueError as e:
print(e) # Output: attempt to get argmax of an empty sequence
Output:
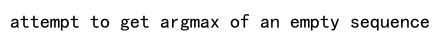
Example 9: Using argmax on a complex array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1+2j, 3+4j, 2+3j])
index_of_max = np.argmax(arr)
print(index_of_max) # Output: 1 (Based on magnitude)
Output:
![]()
Practical Applications of numpy.argmax
The argmax function is widely used in various fields such as data analysis, machine learning, and image processing. Here are a few practical applications:
- Finding the most influential feature: In machine learning,
argmaxcan be used to identify the most important feature of a dataset. - Image processing: In image processing,
argmaxcan help in tasks like locating the brightest point in an image. - Time series analysis: In financial or signal data, finding the time point with the maximum value can be crucial for trend analysis.
Numpy Argmax Conclusion
The numpy.argmax function is a versatile tool in Python’s numpy library. It helps in finding the indices of maximum values across different axes of an array, making it invaluable in data analysis, machine learning, and beyond. With the examples provided, you should have a good understanding of how to use argmax effectively in your projects.