Numpy Array Indexing
Numpy arrays provide a powerful way to store and manipulate data in Python. Indexing in numpy arrays is a critical feature that allows you to access, modify, and manipulate specific elements, rows, columns, or a subarray within a larger array. This article will explore various methods and techniques of indexing in numpy arrays, providing detailed examples to illustrate each concept.
1. Basic Indexing
Basic indexing in numpy is similar to accessing elements in a Python list. It allows you to access elements in the array using their indices.
Example 1: Accessing a single element
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Access the third element
element = arr[2]
print(element)
Output:
![]()
Example 2: Slicing an array
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Slice from index 1 to 3
sub_array = arr[1:4]
print(sub_array)
Output:
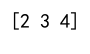
2. Advanced Indexing
Advanced indexing allows you to access multiple non-consecutive indices at once. This can be done using integer arrays or boolean arrays.
Example 3: Integer array indexing
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
# Access elements at indices 1, 3, and 4
selected_elements = arr[[1, 3, 4]]
print(selected_elements)
Output:

Example 4: Boolean array indexing
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
# Create a boolean array
mask = np.array([True, False, True, False, True])
# Access elements where mask is True
selected_elements = arr[mask]
print(selected_elements)
Output:
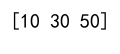
3. Indexing with Conditions
You can use conditions directly within the indexing brackets to select elements that meet certain criteria.
Example 5: Conditional indexing
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
# Select elements greater than 25
selected_elements = arr[arr > 25]
print(selected_elements)
Output:

4. Fancy Indexing
Fancy indexing refers to passing arrays of indices to access multiple array elements at once.
Example 6: Fancy indexing with integer arrays
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
# Define an array of indices
indices = np.array([3, 0, 4])
# Select elements at the specified indices
selected_elements = arr[indices]
print(selected_elements)
Output:
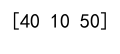
5. Indexing Multi-dimensional Arrays
Indexing multi-dimensional arrays allows you to access specific rows, columns, or sub-arrays.
Example 7: Accessing a row in a 2D array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Access the second row
row = arr[1]
print(row)
Output:
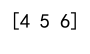
Example 8: Accessing a column in a 2D array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Access the first column
column = arr[:, 0]
print(column)
Output:
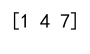
Example 9: Accessing a sub-array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Access a sub-array (2x2 from top left corner)
sub_array = arr[:2, :2]
print(sub_array)
Output:

6. Modifying Elements Using Indexing
Indexing can also be used to modify elements in the array.
Example 10: Modifying an element
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Modify the third element
arr[2] = 30
print(arr)
Output:
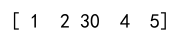
Example 11: Modifying a sub-array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Modify a sub-array
arr[0:2, 1:3] = np.array([[20, 30], [50, 60]])
print(arr)
Output:

7. Using np.ix_ for N-dimensional Indexing
The np.ix_ function allows you to index multiple dimensions of an array simultaneously.
Example 12: Using np.ix_
import numpy as np
# Create a 3D numpy array
arr = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
# Use np.ix_ to select elements
selected_elements = arr[np.ix_([0, 1], [1], [0])]
print(selected_elements)
Output:

8. Ellipsis (...) in Indexing
The ellipsis (...) can be used to represent multiple colons in a multi-dimensional array.
Example 13: Using ellipsis
import numpy as np
# Create a 4D numpy array
arr = np.array([[[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]]])
# Use ellipsis to access elements
selected_elements = arr[..., 1]
print(selected_elements)
Output:

9. Index Arrays with Broadcasting
Numpy’s broadcasting feature allows index arrays to be broadcasted to a common shape, enabling more flexible indexing operations.
Example 14: Indexing with broadcasting
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Create an index array
indices = np.array([0, 2])
# Use broadcasting for complex indexing
selected_elements = arr[:, indices]
print(selected_elements)
Output:

Numpy Array Indexing Conclusion
Numpy array indexing is a versatile tool that enhances the capability to manipulate and analyze data efficiently. By understanding and utilizing the different types of indexing discussed in this article, you can perform complex data manipulations and extractions in a concise and efficient manner. The examples provided demonstrate the flexibility and power of numpy indexing, making it an essential part of any data scientist’s toolkit.