Numpy Clip Min
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is the clip() function. This function is used to limit the values in an array. In this article, we will explore the clip() function with a focus on its use to set a minimum value for elements in an array.
Introduction to Numpy Clip
The clip() function in Numpy is used to clip (limit) the values in an array. You can specify a minimum and a maximum value, and all elements smaller than the minimum value are set to the minimum value, and all elements larger than the maximum value are set to the maximum value.
The syntax of the clip() function is as follows:
numpy.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)
ais the array containing elements to clip.a_minis the minimum value to use for clipping. All values less than this will be set toa_min.a_maxis the maximum value to use for clipping. All values greater than this will be set toa_max.outis an optional array in which to place the result. It must have the same shape as the input array.
Using Clip to Set Minimum Values
Setting a minimum value for an array can be particularly useful in data preprocessing, where you might want to ensure that no values fall below a certain threshold. For example, in image processing, you might want to ensure that no pixel values fall below 0.
Example 1: Basic Clipping
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Clip the array
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
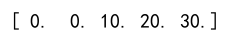
Example 2: Clipping 2D Array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D array
arr = np.array([[-10, 0], [10, 20], [30, -40]])
# Clip the array
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 3: Using Clip Without Specifying a_max
If you only want to set a minimum value and do not wish to limit the maximum, you can use np.inf as a_max.
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Clip the array with no max limit
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
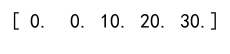
Example 4: Clipping with Negative Minimum
Clipping can also be used with negative minimum values.
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Clip the array with a negative minimum
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=-5, a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
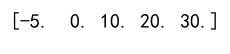
Example 5: Clipping with a Dynamic Minimum
Sometimes, you might want to determine the minimum value dynamically based on some condition or calculation.
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Calculate the minimum dynamically
dynamic_min = np.mean(arr) - np.std(arr)
# Clip the array
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=dynamic_min, a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 6: Clipping with Broadcasting
Numpy’s broadcasting feature allows you to clip arrays of different shapes.
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D array
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Create a minimum array that will be broadcasted
min_values = np.array([0, 1, 2])
# Clip the array
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=min_values[:, np.newaxis], a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
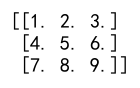
Example 7: Clipping and Reshaping
You can combine clipping with other Numpy operations like reshaping.
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Clip and reshape the array
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf).reshape(5, 1)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 8: Clipping with Complex Conditions
Clipping can be combined with other conditions to perform more complex operations.
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([-10, 0, 10, 20, 30])
# Clip the array based on a complex condition
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, a_min=np.where(arr < 0, -5, 0), a_max=np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
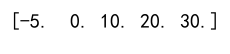
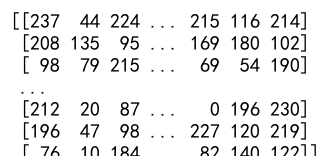
Example 9: Using Clip in Image Processing
Clipping is commonly used in image processing to adjust pixel values.
import numpy as np
# Create a simulated image array
image = np.random.randint(-10, 255, (100, 100))
# Clip the image array to ensure pixel values are within the valid range
clipped_image = np.clip(image, a_min=0, a_max=255)
print(clipped_image)
Output:
Numpy Clip Min Conclusion
In this article, we explored the clip() function in Numpy, focusing on its use to set minimum values for array elements. We provided several examples demonstrating how to use the clip() function in different scenarios, including basic clipping, in-place clipping, clipping with broadcasting, and more. This function is extremely useful in data preprocessing, image processing, and any scenario where you need to enforce value limits on an array.