Concatenate Arrays in NumPy
NumPy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays. One of the essential operations provided by NumPy is the ability to concatenate arrays. Concatenation refers to the process of joining two or more arrays together. In this article, we will explore various ways to concatenate arrays using NumPy, along with detailed examples.
Understanding Concatenation in NumPy
Concatenation in NumPy can be performed using several functions, primarily np.concatenate, np.vstack, np.hstack, and np.dstack. Each of these functions serves different purposes and is suitable for different array structures.
1. np.concatenate
np.concatenate is the most general function for concatenation. It takes a sequence of arrays and joins them along an existing axis.
Example 1: Concatenating One-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3], dtype='int')
b = np.array([4, 5, 6], dtype='int')
# Concatenate arrays
result = np.concatenate((a, b))
print(result)
Output:
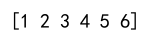
Example 2: Concatenating Two-Dimensional Arrays Along Axis 0
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Concatenate along the first axis (rows)
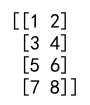
result = np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
print(result)
Output:
Example 3: Concatenating Two-Dimensional Arrays Along Axis 1
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Concatenate along the second axis (columns)
result = np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

2. np.vstack (Vertical Stack)
np.vstack is used to stack arrays vertically, i.e., along the rows.
Example 4: Vertical Stacking of One-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Vertically stack the arrays
result = np.vstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Vertical Stacking of Two-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Vertically stack the arrays
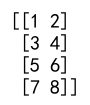
result = np.vstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:
3. np.hstack (Horizontal Stack)
np.hstack is used to stack arrays horizontally, i.e., along the columns.
Example 6: Horizontal Stacking of One-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Horizontally stack the arrays
result = np.hstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:
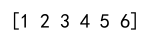
Example 7: Horizontal Stacking of Two-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Horizontally stack the arrays
result = np.hstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:

4. np.dstack (Depth Stack)
np.dstack is used to stack arrays along the third axis (depth).
Example 8: Depth Stacking of One-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Depth stack the arrays
result = np.dstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Depth Stacking of Two-Dimensional Arrays
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Depth stack the arrays
result = np.dstack((a, b))
print(result)
Output:

Advanced Concatenation Techniques
Beyond simple stacking, NumPy allows for more complex concatenation strategies, such as concatenating along new axes or using conditions.
5. Concatenating Along a New Axis
Using np.newaxis or np.expand_dims, you can concatenate arrays along a new axis.
Example 10: Concatenating Using np.newaxis
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Concatenate along a new axis
result = np.concatenate((a[:, np.newaxis], b[:, np.newaxis]), axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

Example 11: Concatenating Using np.expand_dims
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Use np.expand_dims to add a new axis and concatenate
a_expanded = np.expand_dims(a, axis=1)
b_expanded = np.expand_dims(b, axis=1)
result = np.concatenate((a_expanded, b_expanded), axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

6. Conditional Concatenation
Sometimes, you might want to concatenate arrays based on certain conditions. This can be achieved using boolean indexing.
Example 12: Conditional Concatenation
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
b = np.array([5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
# Create a condition
condition = np.array([True, False, True, False, True])
# Concatenate based on condition
result = np.concatenate([a[condition], b[~condition]])
print(result)
Output:
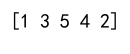
Concatenate Arrays in NumPy Conclusion
Concatenating arrays is a fundamental operation in data manipulation and analysis, making it a crucial skill for data scientists and engineers working with Python. NumPy provides versatile tools that allow for efficient and flexible array concatenation, catering to a wide range of needs. Whether you are working with simple one-dimensional arrays or complex multi-dimensional data structures, understanding how to effectively concatenate arrays will significantly enhance your data processing capabilities.