Numpy argmax get all indices
Numpy is a powerful library for numerical computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the most commonly used functions in Numpy is argmax, which returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis.
However, argmax only returns the first occurrence of the maximum value. In many cases, we might want to get all the indices of the maximum value. This article will show you how to do that using Numpy.
Basic usage of argmax
Before we dive into getting all indices of the maximum value, let’s first understand the basic usage of argmax. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 2, 1])
print(np.argmax(a))
Output:
![]()
This will output 2, which is the index of the maximum value 3 in the array a.
Get all indices of the maximum value
To get all indices of the maximum value, we can use the numpy.where function. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1])
max_indices = np.where(a == np.max(a))
print(max_indices)
Output:

This will output (array([2, 3]),), which are the indices of the maximum value 3 in the array a.
Get all indices of the maximum value in a 2D array
The above example works for 1D arrays. For 2D arrays, we can still use the numpy.where function, but we need to provide the numpy.unravel_index function to convert the flat indices into a tuple of coordinate arrays. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
max_indices = np.unravel_index(np.where(a == np.max(a)), a.shape)
print(max_indices)
Output:

This will output (array([2]), array([2])), which are the indices of the maximum value 9 in the 2D array a.
Get all indices of the maximum value along an axis
If we want to get all indices of the maximum value along an axis, we can use the numpy.argmax function with the axis parameter. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
max_indices = np.argmax(a, axis=0)
print(max_indices)
Output:
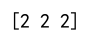
This will output array([2, 2, 2]), which are the indices of the maximum values along the column axis in the 2D array a.
However, this will only return the first occurrence of the maximum value along the axis. To get all occurrences, we can use a combination of the numpy.where and numpy.argmax functions. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
max_indices = np.where(a == np.max(a, axis=0))
print(max_indices)
Output:
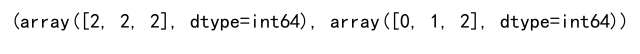
This will output (array([2, 2, 2]), array([0, 1, 2])), which are the indices of the maximum values along the column axis in the 2D array a.
Get all indices of the maximum value in a structured array
Numpy also supports structured arrays, which are arrays with structured data types. To get all indices of the maximum value in a structured array, we can use the numpy.argmax function with the field parameter. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
dtype = [('name', 'S10'), ('height', float), ('age', int)]
values = [('Arthur', 1.8, 41), ('Lancelot', 1.9, 38), ('Galahad', 1.7, 38)]
a = np.array(values, dtype=dtype)
max_indices = np.argmax(a['height'])
print(max_indices)
Output:
![]()
This will output 1, which is the index of the maximum value in the ‘height’ field in the structured array a.
However, this will only return the first occurrence of the maximum value. To get all occurrences, we can use the numpy.where function. Here is an example:
import numpy as np
dtype = [('name', 'S10'), ('height', float), ('age', int)]
values = [('Arthur', 1.8, 41), ('Lancelot', 1.9, 38), ('Galahad', 1.7, 38)]
a = np.array(values, dtype=dtype)
max_indices = np.where(a['height'] == np.max(a['height']))
print(max_indices)
Output:

This will output (array([1]),), which are the indices of the maximum value in the ‘height’ field in the structured array a.
In conclusion, Numpy provides powerful functions to get the indices of the maximum values in an array. By combining these functions, we can easily get all indices of the maximum value in various types of arrays.