Numpy Array Type
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the key features of Numpy is its N-dimensional array type, ndarray. This article will explore the ndarray in detail, including how to create and manipulate these arrays using Numpy.
1. Introduction to Numpy ndarray
The Numpy ndarray is a grid of values, all of the same type, and is indexed by a tuple of nonnegative integers. The number of dimensions is the rank of the array; the shape of an array is a tuple of integers giving the size of the array along each dimension.
Example 1: Creating a Numpy Array
import numpy as np
# Create a numpy array from a Python list
array_example = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=np.int32)
print(array_example)
Output:
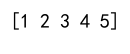
Example 2: Creating a Multi-dimensional Array
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D numpy array from a list of lists
array_2d_example = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], dtype=np.int32)
print(array_2d_example)
Output:

2. Data Types in Numpy
Numpy supports a much greater variety of numerical types than Python does. This section covers the most common types used in Numpy arrays.
Example 3: Specifying the Data Type
import numpy as np
# Create an array with data type float
float_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=np.float64)
print(float_array)
Output:

Example 4: Complex Numbers
import numpy as np
# Create an array of complex numbers
complex_array = np.array([1+2j, 3+4j, 5+6j])
print(complex_array)
Output:
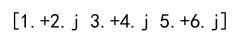
3. Array Attributes
Each array has attributes ndim (the number of dimensions), shape (the size of each dimension), and dtype (the data type of the array).
Example 5: Array Attributes
import numpy as np
# Create a 3D array
array_3d = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
print(array_3d.ndim) # Number of dimensions
print(array_3d.shape) # Shape of the array
print(array_3d.dtype) # Data type of the array
Output:

4. Indexing and Slicing
Numpy offers several ways to index into arrays.
Example 6: Simple Indexing
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D array
array_indexing = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
print(array_indexing[1, 2]) # Access the element at row 1, column 2
Output:
![]()
Example 7: Slicing
import numpy as np
# Slice elements from the second row
slice_example = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
print(slice_example[1, :]) # Slice the second row
Output:
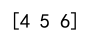
5. Reshaping Arrays
Changing the shape of an existing array is a common operation.
Example 8: Reshape an Array
import numpy as np
# Reshape a 1D array to a 2D array with 3 rows and 2 columns
reshape_example = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
new_shape = reshape_example.reshape((3, 2))
print(new_shape)
Output:

6. Combining Arrays
Numpy provides several functions to combine arrays.
Example 9: Concatenate Arrays
import numpy as np
# Concatenate two arrays
array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
array2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
concatenated_array = np.concatenate((array1, array2))
print(concatenated_array)
Output:
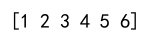
Example 10: Stacking Arrays
import numpy as np
# Stack arrays vertically
array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
array2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
stacked_array = np.vstack((array1, array2))
print(stacked_array)
Output:

7. Splitting Arrays
Splitting is the opposite of combining arrays.
Example 11: Splitting an Array
import numpy as np
# Split an array into three equally shaped arrays
split_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
new_arrays = np.split(split_array, 3)
print(new_arrays)
Output:
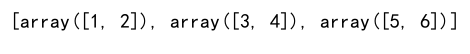
8. Broadcasting
Broadcasting is a powerful mechanism that allows numpy to work with arrays of different shapes when performing arithmetic operations.
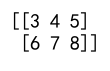
Example 12: Broadcasting Example
import numpy as np
# Add a scalar to a 2D array
broadcast_array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
result = broadcast_array + 2
print(result)
Output:
9. Universal Functions (ufunc)
Numpy provides a set of universal functions that operate elementwise on arrays.
Example 13: Universal Function – np.add
import numpy as np
# Use the add ufunc
array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
array2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
added_array = np.add(array1, array2)
print(added_array)
Output:
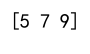
10. Aggregation Functions
Numpy also provides functions to perform aggregate operations along the array.
Example 14: Sum of Array Elements
import numpy as np
# Compute the sum of all elements in the array
sum_array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
total_sum = np.sum(sum_array)
print(total_sum)
Output:
![]()
11. Saving and Loading Arrays
Numpy allows you to save arrays to disk and load them back.
Example 15: Save and Load a Numpy Array
import numpy as np
# Save an array to a binary file in NumPy `.npy` format
array_to_save = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
np.save('numpyarray_com.npy', array_to_save)
# Load the array from the file
loaded_array = np.load('numpyarray_com.npy')
print(loaded_array)
Output:
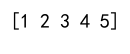
Numpy Array Type Conclusion
This article has covered the basics and some advanced topics related to the Numpy ndarray. Understanding these concepts is crucial for anyone working with numerical data in Python. By mastering the creation, manipulation, and functions of Numpy arrays, you can significantly speed up the data analysis process.