Numpy Clip Array
Numpy is a fundamental library for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One useful function provided by Numpy is clip, which is used to limit the values in an array.
Introduction to Numpy Clip
The clip function is used to limit the values in an array to a specified range. This is particularly useful when you want to remove outliers or limit the range of data for better visualization or further analysis. The function takes three main arguments: the array, a minimum value, and a maximum value. All values below the minimum are set to the minimum, and all values above the maximum are set to the maximum.
Syntax of Clip Function
numpy.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)
a: array_like, Input array.a_min: scalar or array_like, Minimum value.a_max: scalar or array_like, Maximum value. Ifa_minora_maxare array_like, then they will be broadcasted to the shape ofa.out: ndarray, optional, The results will be placed in this array. It may be the input array for in-place clipping.
Examples of Using Numpy Clip
Example 1: Basic Clipping
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 3, 7)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
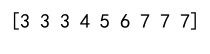
Example 2: Clipping with Scalar Minimum and Maximum
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(10) * 10 # Random array of 10 elements from 0 to 10
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 2, 8)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 3: Clipping with Array-like Minimum and Maximum
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(10) * 100 # Random array of 10 elements from 0 to 100
min_limits = np.linspace(10, 50, 10)
max_limits = np.linspace(60, 100, 10)
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, min_limits, max_limits)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 4: In-place Clipping
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
np.clip(arr, 3, 7, out=arr)
print(arr)
Output:
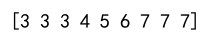
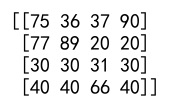
Example 5: Clipping Multidimensional Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randint(1, 100, (5, 5))
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 10, 90)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 6: Using Clip with Negative Values
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([-10, -5, 0, 5, 10])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, -3, 3)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 7: Clipping with No Upper Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 3, np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
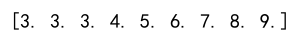
Example 8: Clipping with No Lower Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, -np.inf, 7)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
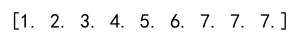
Example 9: Broadcasting in Clipping
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randint(1, 100, (4, 4))
min_limits = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, min_limits[:, None], 90)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
Example 10: Clipping Complex Numbers
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1+2j, 2+3j, 3+4j, 4+5j, 5+6j])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 1+2j, 4+5j)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
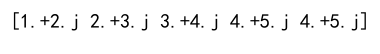
Numpy Clip Array Conclusion
The clip function in Numpy is a powerful tool for managing the range of data in arrays. It allows for both simple and complex clipping operations, including the ability to handle scalars, arrays, and even complex numbers. This function is particularly useful in data preprocessing, where limiting the range of data can help in achieving better performance in machine learning models or clearer visualizations in data analysis.