Numpy Clip
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is clip, which is used to limit the values in an array.
Introduction to Numpy Clip
The clip function is used to limit the values in an array to a specified range. This is particularly useful when you want to avoid outliers or values that exceed a certain threshold in your data processing tasks. The function takes three main arguments: the array, a minimum value, and a maximum value. All values in the array that are below the minimum value are set to the minimum value, and all values that are above the maximum value are set to the maximum value.
Syntax of Numpy Clip
The basic syntax of the clip function in Numpy is as follows:
numpy.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)
a: Array containing elements to clip.a_min: Minimum value.a_max: Maximum value.out: An optional array in which to place the result. The default isNone; if provided, it must have a shape that the inputs broadcast to.
Examples of Numpy Clip
Let’s explore some examples to understand how to use the clip function in various scenarios.
Example 1: Basic Usage of Clip
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 3, 7)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
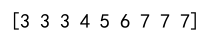
Example 2: Clipping 2D Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 2, 8)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 3: Using Clip with Negative Values
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, -2, 2)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
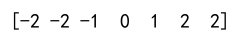
Example 4: Clipping with No Upper Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 15, np.inf)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
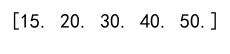
Example 5: Clipping with No Lower Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, -np.inf, 35)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
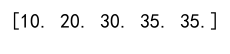
Example 6: Clipping with Out Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
out_arr = np.empty_like(arr)
np.clip(arr, 2, 4, out=out_arr)
print(out_arr)
Output:
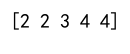
Example 7: Clipping Complex Numbers
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1+2j, 2+3j, 3+4j, 4+5j])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 1+2j, 3+4j)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
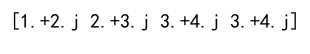
Example 8: Clipping Using Scalars
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1.1, 2.5, 3.7, 4.6, 5.8])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 2.5, 4.6)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
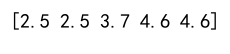
Example 9: Clipping with Broadcasting
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
min_vals = np.array([1, 2, 3])
max_vals = np.array([7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, min_vals[:, np.newaxis], max_vals[:, np.newaxis])
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 10: Clipping with Different Shapes
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
min_vals = np.array([1, 4, 7])
max_vals = np.array([3, 6, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, min_vals[:, np.newaxis], max_vals[:, np.newaxis])
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Numpy Clip Conclusion
The clip function in Numpy is a powerful tool for managing data by limiting values to a specified range. It can handle arrays of any shape and size, and supports broadcasting, which makes it versatile for various data processing tasks. By using clip, you can ensure that your data stays within the desired boundaries, improving the robustness and reliability of your computations.