Numpy Clip Example
Numpy is a fundamental library for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. One of the useful functions provided by Numpy is clip(). This function is used to limit the values in an array to a specified range. In this article, we will explore the clip() function in detail, providing numerous examples to illustrate its use.
Introduction to Numpy Clip
The clip() function takes an array and bounds as its input and returns a new array where every element is clipped to the bounds provided. The syntax of the function is:
numpy.clip(a, a_min, a_max, out=None)
ais the array containing elements to clip.a_minis the minimum value to clip to.a_maxis the maximum value to clip to.outis an optional array in which to place the result.
If an element in the array a is smaller than a_min, it will be replaced with a_min. If an element in the array a is larger than a_max, it will be replaced with a_max.
Example 1: Basic Usage of Clip
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 3, 7)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
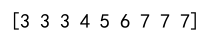
Example 2: Clipping 2D Arrays
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 2, 8)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 3: Using Clip with Negative Bounds
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([-12, 0, 10, -5, 8, -1])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, -10, 10)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
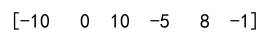
Example 4: Clipping with No Upper Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 3, None)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
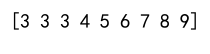
Example 5: Clipping with No Lower Bound
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, None, 7)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
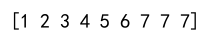
Example 6: Using Clip with Out Parameter
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
out_arr = np.empty_like(arr)
np.clip(arr, 3, 7, out=out_arr)
print(out_arr)
Output:
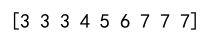
Example 7: Clipping Multidimensional Array
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randint(1, 100, (5, 5))
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 10, 90)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
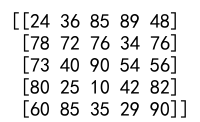
Example 8: Clipping with Scalars
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1.1, 2.5, 3.8, 4.6, 5.9])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, 2.0, 5.0)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:

Example 9: Clipping with Different Minimum and Maximum for Each Element
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
min_bounds = np.array([1, 1, 2, 2, 3])
max_bounds = np.array([3, 3, 4, 4, 5])
clipped_arr = np.clip(arr, min_bounds, max_bounds)
print(clipped_arr)
Output:
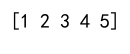
Example 10: Using Clip in a Real-world Scenario
import numpy as np
# Simulating sensor data that might have erroneous values
sensor_data = np.array([102, 99, 450, 130, 120, 110, 115, 500, 106, 109])
# Assuming sensor range should be between 100 and 150
corrected_data = np.clip(sensor_data, 100, 150)
print(corrected_data)
Output:
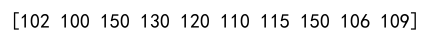
Numpy Clip Example Conclusion
The clip() function in Numpy is a powerful tool for managing data ranges in arrays. It ensures that all elements in an array adhere to specified minimum and maximum bounds. This can be particularly useful in data cleaning processes where certain values may be out of the expected range due to measurement errors or other anomalies. By using clip(), you can ensure that your data remains robust and reliable for analysis.