Numpy Append vs Concatenate
Numpy is a powerful library for numerical computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. Two of the most commonly used functions in Numpy are append and concatenate. These functions are used to combine arrays in different ways. In this article, we will discuss the differences between these two functions, and provide examples of how to use them.
Numpy Append
The numpy.append function is used to merge two arrays. It takes two arrays as arguments and returns a new array that contains all the elements of the first array followed by all the elements of the second array.
Here is an example of how to use numpy.append:
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Append arr2 to arr1
result = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(result)
Output:
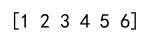
In this example, numpy.append combines arr1 and arr2 into a single array. Note that numpy.append does not modify the original arrays.
You can also use numpy.append to add a single element to an array:
import numpy as np
# Create an array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
# Append 4 to the array
result = np.append(arr, 4)
print(result)
Output:
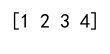
In this example, numpy.append adds the number 4 to the end of arr.
Numpy Concatenate
The numpy.concatenate function is used to join two or more arrays along an existing axis. It takes a sequence of arrays as its first argument, and an optional axis argument that specifies the axis along which the arrays should be joined.
Here is an example of how to use numpy.concatenate:
import numpy as np
# Create two arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2
result = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
print(result)
Output:
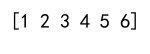
In this example, numpy.concatenate combines arr1 and arr2 into a single array. Note that numpy.concatenate does not modify the original arrays.
You can also use numpy.concatenate to join arrays along a specific axis:
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2 along the first axis
result = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2), axis=0)
print(result)
Output:
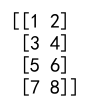
In this example, numpy.concatenate joins arr1 and arr2 along the first axis (rows).
Differences Between Numpy Append and Concatenate
While numpy.append and numpy.concatenate can often be used interchangeably, there are some key differences between these two functions:
numpy.appendcan only combine two arrays, whilenumpy.concatenatecan combine any number of arrays.-
numpy.appendalways returns a 1D array, regardless of the dimensions of the input arrays. On the other hand,numpy.concatenatepreserves the dimensions of the input arrays. -
numpy.appendis a simpler function and is easier to use for beginners. However,numpy.concatenateis more flexible and powerful, and is often preferred by more experienced users.
Here are some examples that illustrate these differences:
import numpy as np
# Create three arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr3 = np.array([7, 8, 9])
# Append arr2 and arr3 to arr1
result = np.append(arr1, [arr2, arr3])
print(result)
Output:
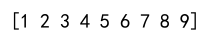
In this example, numpy.append combines arr1, arr2, and arr3 into a single 1D array.
import numpy as np
# Create three arrays
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([4, 5, 6])
arr3 = np.array([7, 8, 9])
# Concatenate arr1, arr2, and arr3
result = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2, arr3))
print(result)
Output:
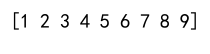
In this example, numpy.concatenate combines arr1, arr2, and arr3 into a single 1D array.
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Append arr2 to arr1
result = np.append(arr1, arr2)
print(result)
Output:
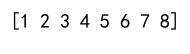
In this example, numpy.append flattens arr1 and arr2 into a single 1D array.
import numpy as np
# Create two 2D arrays
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
arr2 = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# Concatenate arr1 and arr2
result = np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))
print(result)
Output:
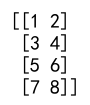
In this example, numpy.concatenate preserves the 2D structure of arr1 and arr2.
In conclusion, while numpy.append and numpy.concatenate are similar, they have different use cases. numpy.append is simpler and easier to use, but numpy.concatenate is more flexible and powerful. You should choose the function that best suits your needs.