Create Numpy Array
Numpy is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays. This article will guide you through various ways to create Numpy arrays, which are essential for data manipulation and scientific calculations in Python.
1. Importing Numpy
Before you can create or manipulate any Numpy arrays, you need to import the Numpy library. If you haven’t installed Numpy yet, you can do so using pip:
pip install numpy
Once installed, you can import it into your Python script:
import numpy as np
2. Creating Numpy Arrays from Python Lists
The simplest way to create a Numpy array is from a regular Python list or a list of lists.
Example 1: Creating a 1D Array
import numpy as np
array_1d = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(array_1d)
Output:
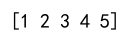
Example 2: Creating a 2D Array
import numpy as np
array_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
print(array_2d)
Output:

3. Using Built-in Numpy Functions
Numpy provides several functions to generate arrays of various forms.
Example 3: np.zeros
Creates an array filled with zeros.
import numpy as np
zeros_array = np.zeros((3, 4))
print(zeros_array)
Output:

Example 4: np.ones
Creates an array filled with ones.
import numpy as np
ones_array = np.ones((2, 3))
print(ones_array)
Output:

Example 5: np.arange
Creates an array with values in a specified range.
import numpy as np
range_array = np.arange(0, 10, 2)
print(range_array)
Output:
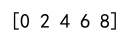
Example 6: np.linspace
Creates an array with a specified number of elements, and spaced equally between the specified beginning and end values.
import numpy as np
linspace_array = np.linspace(0, 1, num=5)
print(linspace_array)
Output:
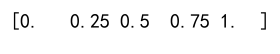
Example 7: np.full
Creates an array filled with a specified value.
import numpy as np
full_array = np.full((3, 5), 7)
print(full_array)
Output:
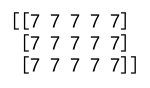
Example 8: np.eye
Creates an identity matrix.
import numpy as np
identity_matrix = np.eye(4)
print(identity_matrix)
Output:

Example 9: np.random.rand
Creates an array of the given shape and populates it with random samples from a uniform distribution over [0, 1).
import numpy as np
random_array = np.random.rand(3, 2)
print(random_array)
Output:

Example 10: np.random.randint
Creates an array of specified shape and fills it with random integers.
import numpy as np
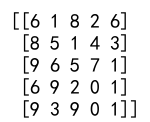
random_int_array = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(5, 5))
print(random_int_array)
Output:
4. Array Attributes
After creating arrays, it’s useful to understand some basic attributes of arrays.
Example 11: Array Shape
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(array.shape)
Output:
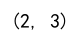
Example 12: Array Size
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(array.size)
Output:
![]()
Example 13: Array Data Type
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(array.dtype)
Output:

5. Reshaping Arrays
Changing the shape of an existing array.
Example 14: np.reshape
import numpy as np
array = np.arange(8)
reshaped_array = np.reshape(array, (2, 4))
print(reshaped_array)
Output:

Example 15: np.transpose
import numpy as np
array = np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5)
transposed_array = np.transpose(array)
print(transposed_array)
Output:

6. Special Case Arrays
Example 16: np.empty
Creates an uninitialized array of specified shape and dtype.
import numpy as np
empty_array = np.empty((3, 3))
print(empty_array)
Output:

Example 17: np.zeros_like
Creates an array of zeros with the same shape and type as a given array.
import numpy as np
array1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
zeros_like_array = np.zeros_like(array1)
print(zeros_like_array)
Output:

Example 18: np.ones_like
Creates an array of ones with the same shape and type as a given array.
import numpy as np
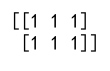
array1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
ones_like_array = np.ones_like(array1)
print(ones_like_array)
Output:
Example 19: np.diag
Creates a diagonal array.
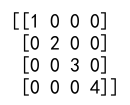
import numpy as np
diag_array = np.diag([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(diag_array)
Output:
Example 20: np.tile
Repeats an array a specified number of times.
import numpy as np
array = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
tiled_array = np.tile(array, (2, 3))
print(tiled_array)
Output:

Create Numpy Array Conclusion
This article has covered a variety of methods to create Numpy arrays, which are the backbone of numerical computing in Python. Understanding these basics will help you perform more complex operations and utilize other features of the Numpy library effectively.